- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: MVC 3
- Hits: 8771
Or other logs.
In my local environment following code worked:
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Diagnostics.Management;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.ServiceRuntime;
namespace MvcWebRole1
{
public class WebRole : RoleEntryPoint
{
public override void Run()
{
SetLogging();
base.Run();
}
public override bool OnStart()
{
return base.OnStart();
}
protected virtual void SetLogging()
{
if (RoleEnvironment.IsAvailable)
{
string wadConnectionString = "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Plugins.Diagnostics.ConnectionString";
//CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse("DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=myAccountName;AccountKey=myAccountKey");
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse("UseDevelopmentStorage=true");
RoleInstanceDiagnosticManager roleInstanceDiagnosticManager = storageAccount.CreateRoleInstanceDiagnosticManager(RoleEnvironment.DeploymentId, RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.Role.Name, RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.Id);
DiagnosticMonitorConfiguration config = DiagnosticMonitor.GetDefaultInitialConfiguration();
config.Logs.ScheduledTransferPeriod = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1);
config.Logs.ScheduledTransferLogLevelFilter = LogLevel.Undefined;
roleInstanceDiagnosticManager.SetCurrentConfiguration(config);
}
}
}
}
Part which is commented:
//CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse("DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=myAccountName;AccountKey=myAccountKey");
Is in use for the Azure, if you want to upload to Azure, then AccountName and AccountKey has to be changed, if anything from these two is wrong, Azure will not report a problem, but virtual machine will not be started.
Also, instead of
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse("UseDevelopmentStorage=true");
It can be:
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(RoleEnvironment.GetConfigurationSettingValue(wadConnectionString));
Also, in local environment, if WadLogsTable is not populated, then reset Azure storage emulator (you will delete all tables and data you have in local storage), and also restart computer, obviously some service has to be restarted, but I don't know which one exactly... and wait at least 3 minutes, while application is started (debugged).
Only TraceError will be logged, and it should be somewhere in controller, because in OnStart will not work.
---
Another solution is this code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Diagnostics.Management;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.ServiceRuntime;
namespace MvcWebRole1
{
public class WebRole : RoleEntryPoint
{
public override bool OnStart()
{
// For information on handling configuration changes
// see the MSDN topic at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=166357.
// instantiate and add a new diagnostic monitor trace listener
// before doing this, you should make sure no listeners are defined in your web.config or app.config
var tempListener = new DiagnosticMonitorTraceListener();
Trace.Listeners.Add(tempListener);
// creates a diagnostic manager instance based on an azure storage account
// before doing this, setup a storage account using the azure web portal
string connectionStringName = "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Plugins.Diagnostics.ConnectionString";
var storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(RoleEnvironment.GetConfigurationSettingValue(connectionStringName));
var roleInstanceDiagnosticManager = storageAccount.CreateRoleInstanceDiagnosticManager(RoleEnvironment.DeploymentId,
RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.Role.Name, RoleEnvironment.CurrentRoleInstance.Id);
// setup the basic logging configuration options
// ScheduledTransferPeriod is how often the trace log is copied to the storage account tables
// ScheduledTransferLogLevelFilter is the filter on the messages to copy
// BufferQuotaInMB is how much space is available to the local buffer (when limit is reached, old data is purged)
var config = roleInstanceDiagnosticManager.GetCurrentConfiguration();
config.Logs.ScheduledTransferPeriod = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1.0);
config.Logs.ScheduledTransferLogLevelFilter = LogLevel.Undefined;
config.Logs.BufferQuotaInMB = 5;
// setup the windows event log configuration options
// adds the System and Application level windows event logs to the sources
// other options are the same as the basic logging
config.WindowsEventLog.DataSources.Add("System!*");
config.WindowsEventLog.DataSources.Add("Application!*");
config.WindowsEventLog.ScheduledTransferPeriod = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1.0);
config.WindowsEventLog.ScheduledTransferLogLevelFilter = LogLevel.Undefined;
roleInstanceDiagnosticManager.SetCurrentConfiguration(config);
return base.OnStart();
}
}
}
More details can be found here.
Lines of code:
config.WindowsEventLog.DataSources.Add("System!*");
config.WindowsEventLog.DataSources.Add("Application!*");
Will create Windows Event Logs, to create WADLogsTable I am not exactly sure which DataSource has to be added. This solution is using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Plugins.Diagnostics.ConnectionString, which can be found in ServiceConfiguration.Cloud.cscfg, or ServiceConfiguration.Local.cscfg, depending on which you need, local or cloud deployment.
Also, don't forget to set level of monitoring to verbose:
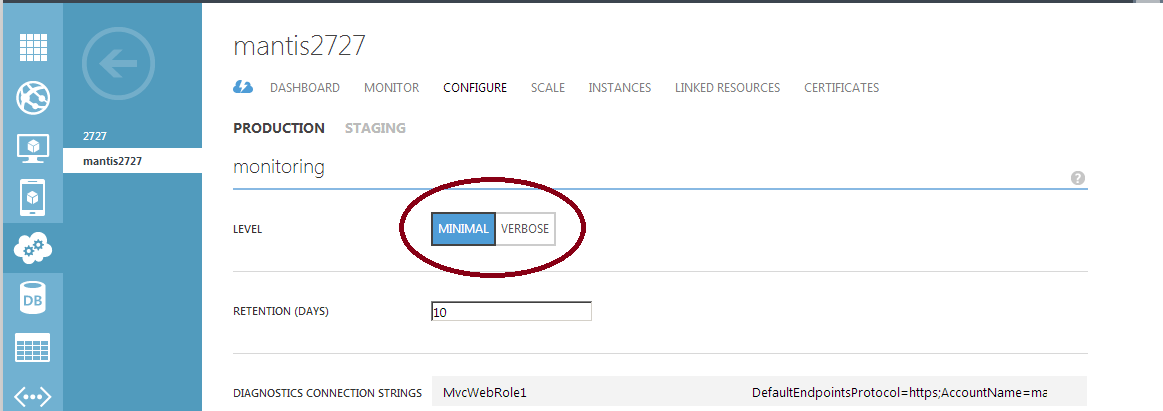
Cloud services -> Configure
---
Just to add my conclusion, actually both ways of creating WadLogsTable are working, and there is no really need for setting level of monitoring, only problem is that trace.Error has to be somewhere in controller (executed on some action), and we have to wait long enough (3 minutes for example)
---
To query WadLog table, using Visual Studio 2010, I can use query like:
PartitionKey ge '0635228657410000000' and Role eq 'MyRole' and Level le 3
Where number 0635228657410000000 is generated with this tool, that tool will generate number like:
635228656810000000, which means that I have to add additional 0 at beginning of that number
And Level is used to show only errors
- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: MVC 3
- Hits: 13787
If you are receiving error like in title, then add in the reference :
EntityFramework
Search for:
EntityFramework.dll
In my case it was in folder:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft ASP.NET\ASP.NET MVC 4\Packages\EntityFramework.5.0.0\lib\net40
--
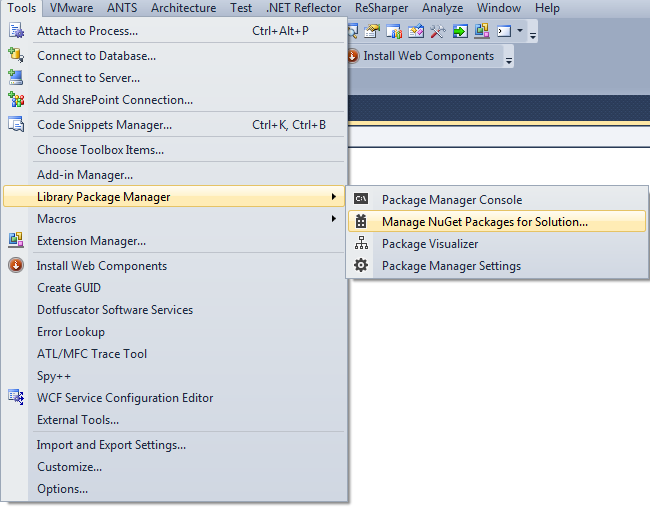
Or you can do it with NuGet. Go to tools -> Library Packager Manager -> Manage NuGet Packages for Solution:
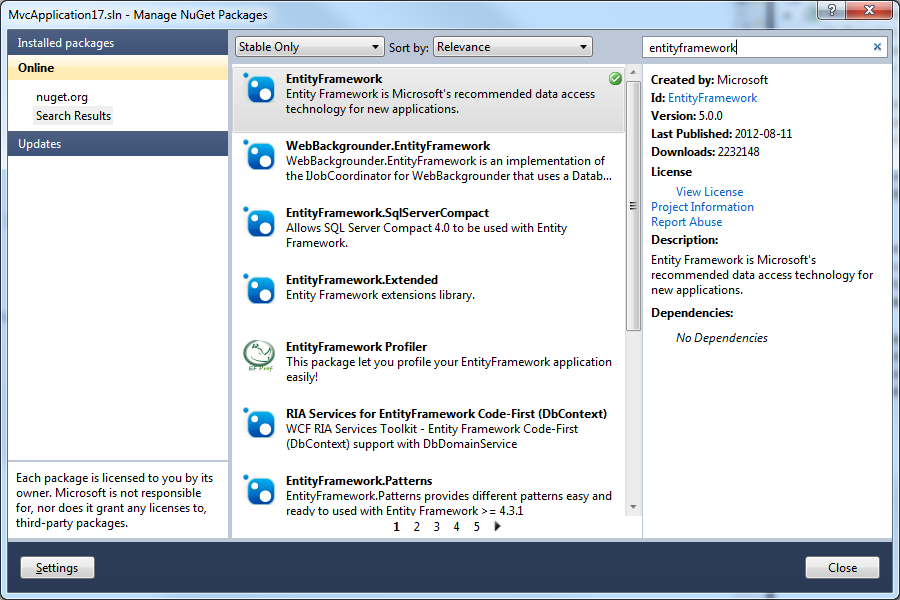
Then search for EntityFramework and install it:
- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: MVC 3
- Hits: 7038
If I understand it good, your controller has to look like:
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
Partner partner = db.Partners.Find(id);
ViewBag.Sifra = new SelectList(db.Partners, "Sifra", "Naziv", partner.Sifra);
return View(partner);
}
view:
@Html.DropDownList("Sifra", null, new { disabled = "disabled"})
- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: MVC 3
- Hits: 5725
If on
Membership.CreateUser(model.UserName, model.Password, model.Email, null, null, true, null, out createStatus);
You are receiveng messages like:
The user instance login flag is not supported on this version of SQL Server. The connection will be closed.
or
Unable to connect to SQL Server database.
Then check in your Web.config file:
add name="AspNetSqlMembershipProvider" type="System.Web.Security.SqlMembershipProvider" connectionStringName="ApplicationServices"
<connectionStrings>
<add name="ApplicationServices"
connectionString="Data Source=MyPC;
Connection string name must be same as name of SqlMembershipProvider connection string.
If after you receive error like:
Could not find stored procedure 'dbo.aspnet_CheckSchemaVersion'.
Then in command prompt execute something like:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\aspnet_regsql.exe -S MyServer -U MyUserId -P myPass -A all -d MyDb
And if you receive error like:
Generating user instances in SQL Server is disabled. Use sp_configure 'user instances enabled' to generate user instances
Then in MS SQL Server execute:
exec sp_configure 'user instances enabled', 1 Reconfigure
and restart server...
